In today’s market, most oxygen machines are molecular sieves oxygen concentrators. It is physical oxygen production and adopts the pressure swing absorption technology to separate the Nitrogen and oxygen from the ambient air. As soon as there is electricity power, it can pump normal air and deliver oxygen to us.
So how does it work? Let’s look at the main parts of an oxygen concentrator.

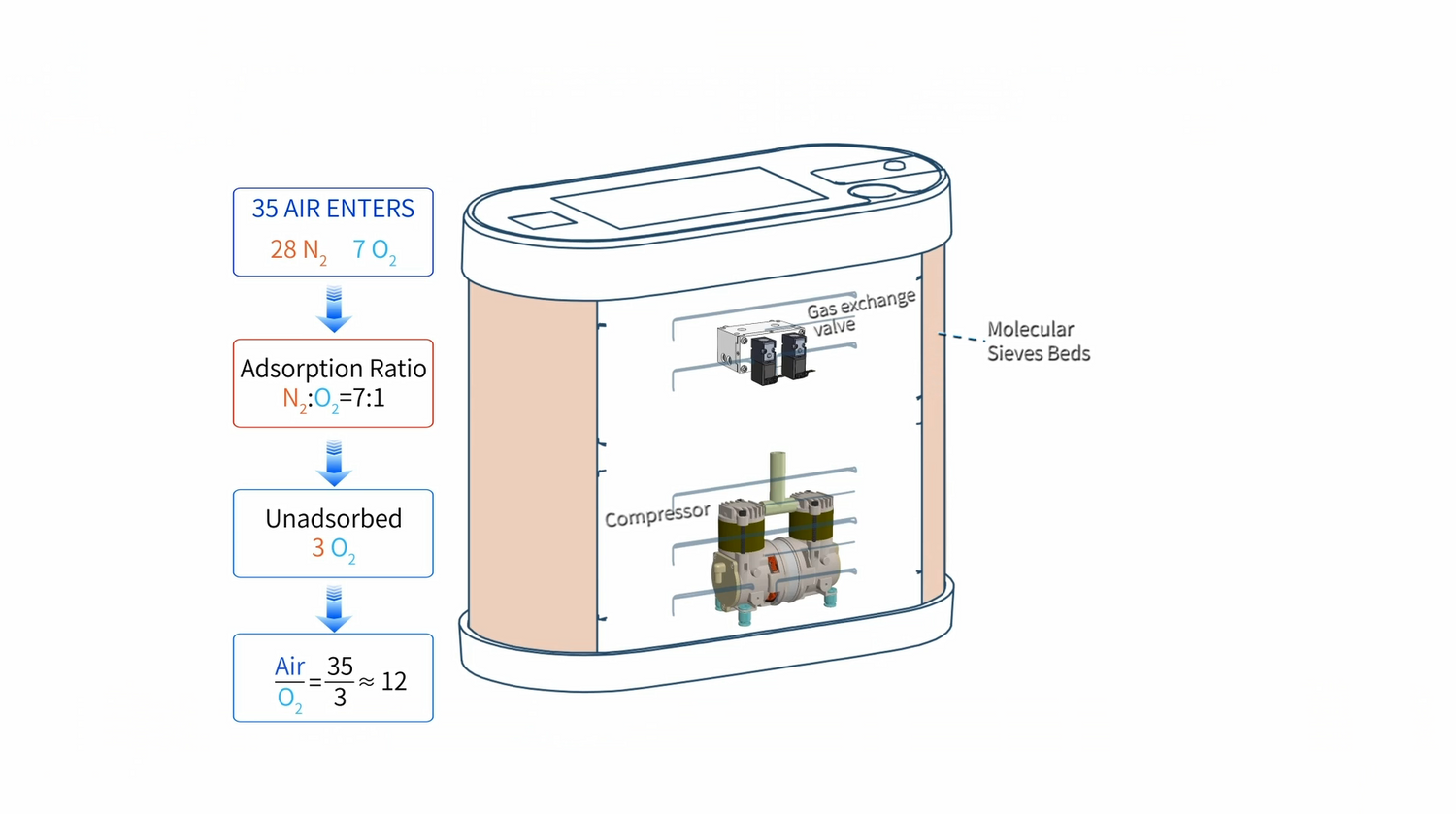
The compressor extracts ambient air firstly and presses the air from normal pressure to high pressure. Next it delivers pressured air into Pressure Swing Adsorption system (PSA). Here PSA system will separate N2 and left O2.
Pressure Swing Adsorption system is made of two cylinders which are filled in molecular sieves. The high pressured air will be filled in one cylinder. Molecular sieves will adsorb all N2 and a small portion of O2 at the same time. Most portion of O2 will go through layers of molecular sieves and be delivered through flowmeter to users. The follow is demonstration video of PSA system working.
<Working video>
This is the whole process of an oxygen concentrator works and how do the air flow into the oxygen concentrator.
There are two factors determine the final amount of oxygen gas.
Factor A: the amount of pressured air. The more pressured air need, the bigger compressor is.
Factor B: the amount of molecular sieves. The more molecular sieves are, the more N2 be absorbed.
If we need more oxygen coming out per minute, it needs more pressured air and more molecular sieves at the same time. Being reflected on parts, the PSA system will become bigger and compressor need to be higher efficiency.
Here is the reason of medical grade oxygen machines is much bigger and heavier.




Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.